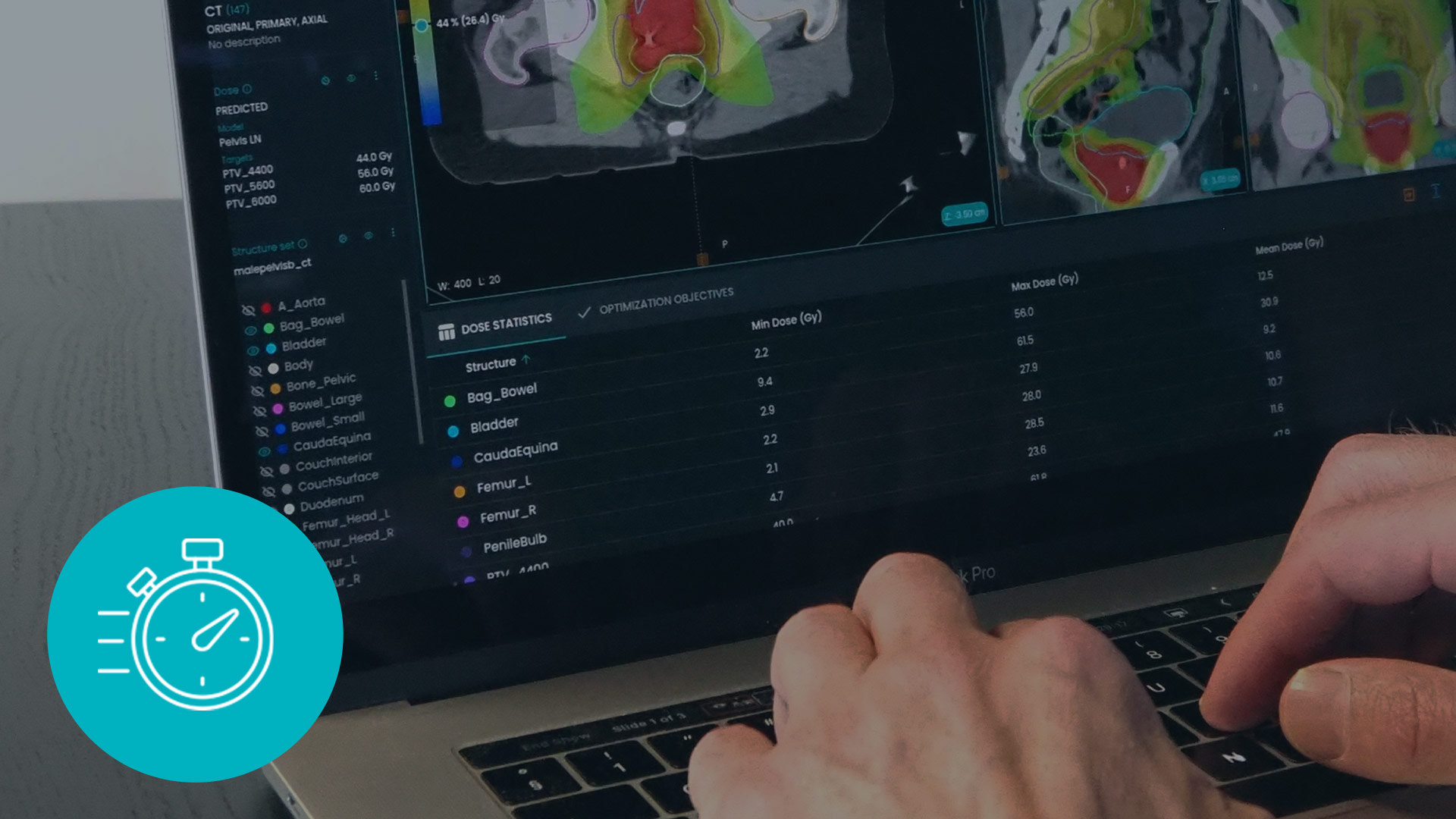
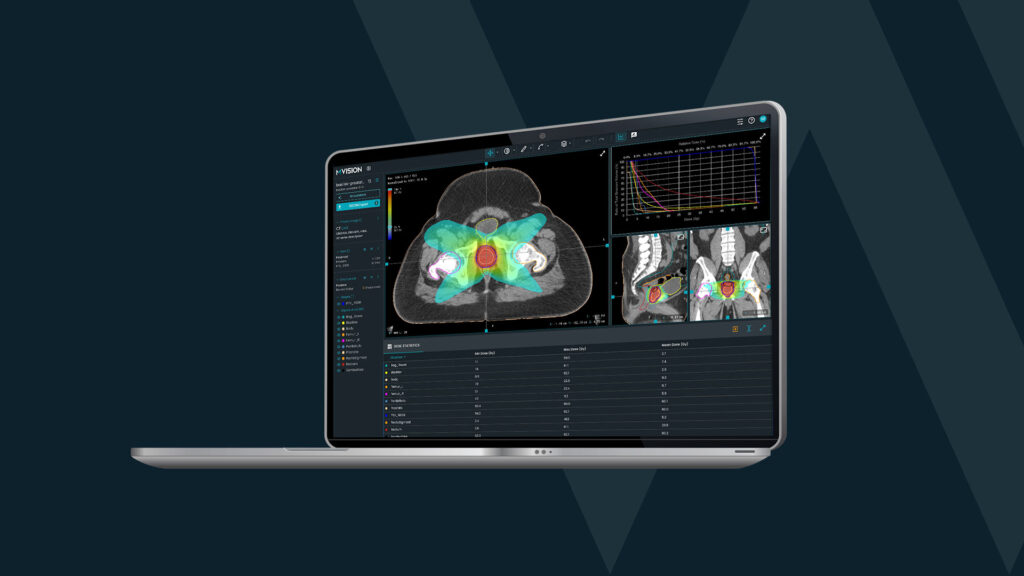
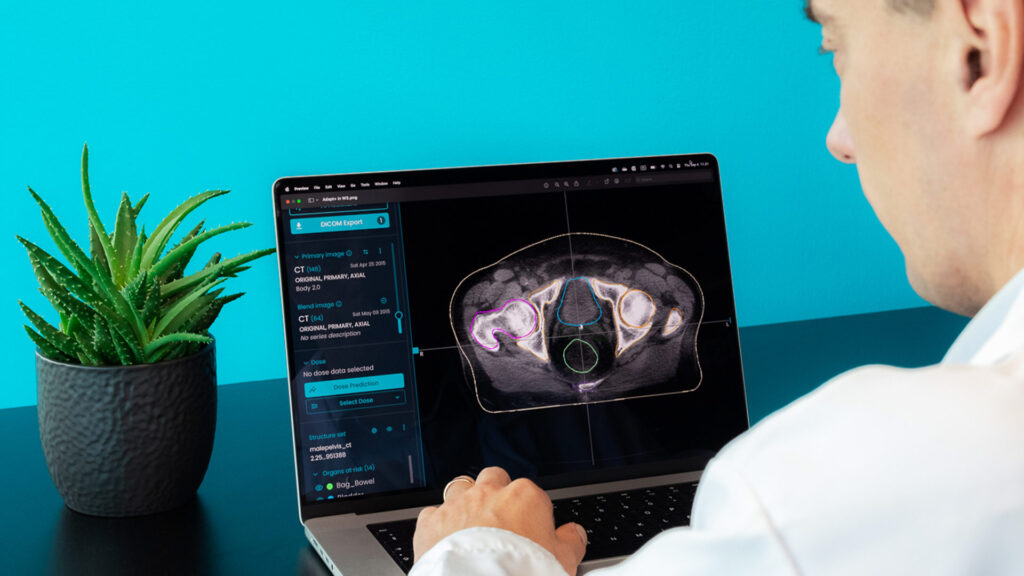
Time is one of the most valuable resources, both for radiotherapy patients and healthcare professionals. For most cancer patients, short delays in the start of treatment will not influence the chance of cure. However, waiting for treatment to start increases distress for many of them (1).
There are multiple causes of suboptimal access to radiation therapy and for the unacceptably long waiting lists (2). One of them is a shortage in the global healthcare workforce, which is expected to worsen by 2050 (3). Artificial intelligence applications represent promising solutions for improving efficacy and quality in cancer care.
Two of the most time-consuming tasks in preparing personalized irradiation plans are contouring and dose planning. Independent studies published in peer-reviewed journals have demonstrated MVision AI Contour+’s value in saving time and improving consistency.
How much time does radiotherapy treatment planning take?
Official websites that provide information for cancer patients mention time intervals from scanning to treatment can range from one to seven days (4) or even from a few days to up to three weeks (7). A significant part of this process is taken up by treatment planning (1,2).
Depending on the anatomical site, the number of volumes, the proximity to organs at risk, clinical factors, irradiation technique, as well as the planner’s experience and skills, there are significant variations in the time required to prepare an irradiation plan.
An interesting analysis was performed by a Chinese team of researchers. The duration of the treatment preparation process and its sub-sections were analyzed for more than 17 000 patients. The mean values were close to 4 days, with longer durations for head and neck cases (5.4 days), compared to the thorax/breast group (3.2 days). Older techniques (2D/3D conformal) required shorter planning times than more sophisticated ones (IMRT, VMAT, Tomotherapy). However, modern techniques allow better precision and decrease the risk of side effects, so they are preferred, despite the longer preparation times. The authors concluded that more than 60% of the total treatment time for cancer patients could potentially be reduced (3).
How can AI help to speed up the process?
Because treatment planning involves a series of complex calculations, combining faster computational methods with data from previous treatment plans can help predict the spatial distribution of radiation doses to specific target volumes.
There are published results of such algorithms that were tested in various clinics across different anatomical sites.
One study, which included 187 rectal cancer cases, showed that the predictions were clinically acceptable and planning time was reduced by 15 minutes (4). Another study analysed 22 postoperative rectal cancer cases and showed a 90% overlap with most of the isodose volumes when comparing AI with the manual planning. The overall mean absolute error was approximately 4% (5).
Promising results were obtained for head and neck cancers as well. The AI-based dose distribution maps were produced within a few seconds, and the results were similar to those from manual planning (6). Another model, this time for prostate cancer, delivered quality results in less than one second, showing great potential for clinical applications in preplanning decision-making and real-time planning (7).
Another study analysed IMRT planning for brain cancers and found that accuracy and similarity in dose prediction provided by the AI-based algorithm were similar to the clinical dose distributions in test patients. Moreover, they were generated very quickly (8).
A systematic review of AI applications in improvement of IMRT and VMAT planning extracted data from 26 articles, showing that automation methods reduce time and increase prediction accuracy. Based on these findings, the authors stated that “Healthcare providers should consider integrating artificial intelligence technologies into their practice to optimize treatment planning and enhance patient care in radiation therapy.” (9)
What does MVision have to offer in this field?
Dose+ is the newest MVision AI solution. It supports Radiation Oncology professionals in quickly estimating the dose distribution map and speeds up treatment planning. Taking into account the incidence of prostate cancer, Mvision AI specialists developed two models for prostate and pelvic lymph node radiotherapy, clinically validated across multiple institutions. The processing time was only 2 minutes, and the clinical acceptance rate was 90%.
Using AI in Radiation oncology brings us closer to achieving faster, more consistent results, empowering healthcare providers to offer better cancer care.
References
- Ye Y, Wang J, Cai S, Fu X, Ji Y. Psychological distress of cancer patients caused by treatment delay during the COVID-19 pandemic in China: A cross-sectional study. Psychooncology. 2022;31(9):1607-1615. doi:10.1002/pon.5946
- Laskar SG, Sinha S, Krishnatry R, Grau C, Mehta M, Agarwal JP. Access to Radiation Therapy: From Local to Global and Equality to Equity. JCO Glob Oncol. 2022;8:e2100358. doi:10.1200/GO.21.00358
- Zhu H, Chua MLK, Chitapanarux I, et al. Global radiotherapy demands and corresponding radiotherapy-professional workforce requirements in 2022 and predicted to 2050: a population-based study. Lancet Glob Health. 2024;12(12):e1945-e1953. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(24)00355-3
- MD Andreson Cancer Centre. Radiation therapy: What to expect? https://www.mdanderson.org/cancerwise/radiation-therapy–what-to-expect.h00-159464790.html#:~:text=How%20soon%20after%20the%20simulation%20will%20I,the%20radiation%20dose%20to%20vital%20healthy%20structures.
- Cancer Research UK. Planning your external radiotherapy. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/treatment/radiotherapy/external/planning/your-planning#:~:text=You%20might%20have%20to%20wait%20a%20few,plan%20the%20treatment%20very%20precisely%20using%20computers.
- Guo C, Huang P, Li Y, Dai J. Accurate method for evaluating the duration of the entire radiotherapy process. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020;21(9):252-258. doi:10.1002/acm2.12959
- Song Y, Hu J, Liu Y, et al. Dose prediction using a deep neural network for accelerated planning of rectal cancer radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2020;149:111-116. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.05.005
- Zhou J, Peng Z, Song Y, et al. A method of using deep learning to predict three-dimensional dose distributions for intensity-modulated radiotherapy of rectal cancer. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020;21(5):26-37. doi:10.1002/acm2.12849
- Li X, Wang C, Sheng Y, et al. An artificial intelligence-driven agent for real-time head-and-neck IMRT plan generation using conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN). Med Phys. 2021;48(6):2714-2723. doi:10.1002/mp.14770
- Jensen PJ, Zhang J, Koontz BF, Wu QJ. A Novel Machine Learning Model for Dose Prediction in Prostate Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy Using Output Initialization and Optimization Priorities. Front Artif Intell. 2021;4:624038. Published 2021 Apr 23. doi:10.3389/frai.2021.624038
- Irannejad M, Abedi I, Lonbani VD, Hassanvand M. Deep-neural network approaches for predicting 3D dose distribution in intensity-modulated radiotherapy of the brain tumors. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024;25(3):e14197. doi:10.1002/acm2.14197
- Zadnorouzi M, Abtahi SMM. Artificial intelligence (AI) applications in improvement of IMRT and VMAT radiotherapy treatment planning processes: A systematic review. Radiography (Lond). 2024;30(6):1530-1535. doi:10.1016/j.radi.2024.09.049