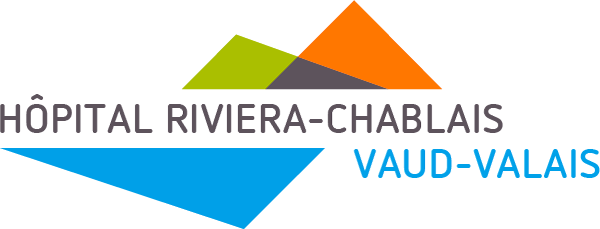Contour+
Guideline-Based AI
Segmentation
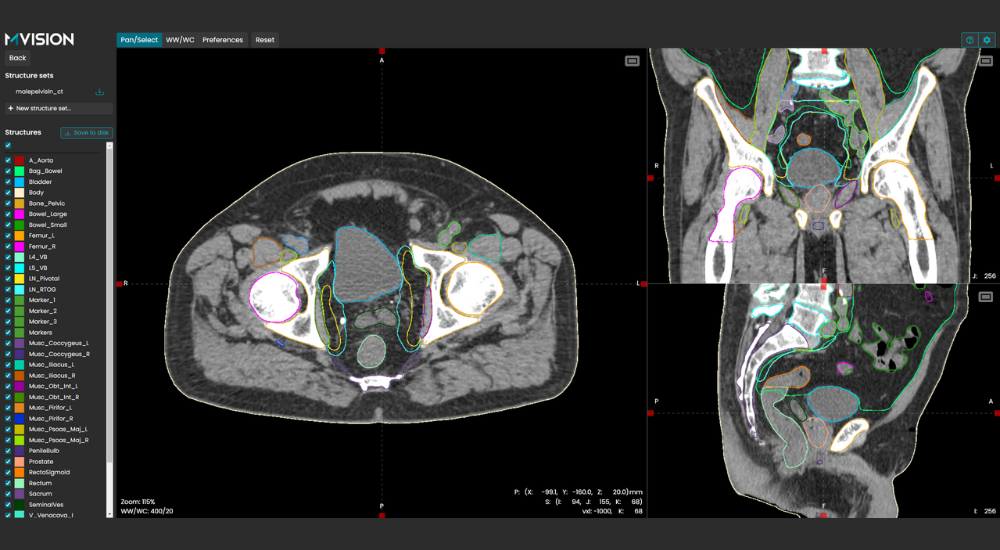
Automatic Contouring for Radiation Therapy
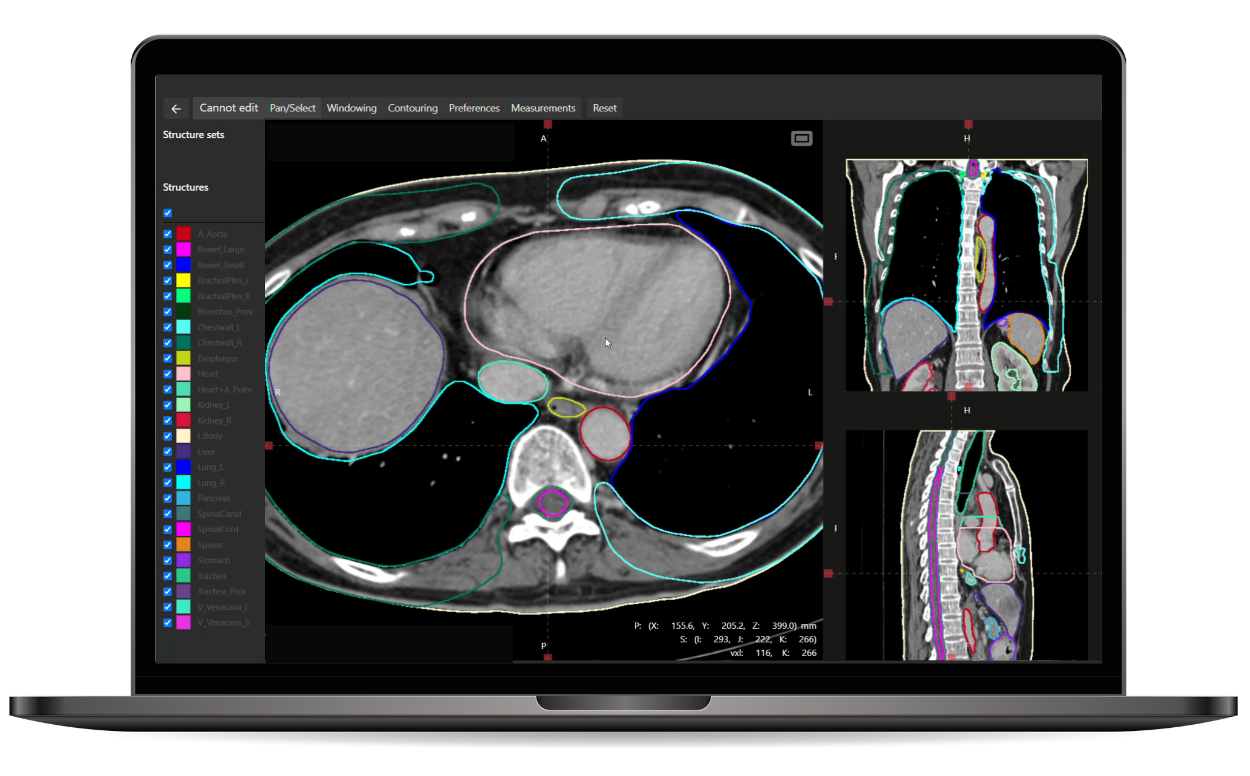
Contour+ speeds up contouring, guides toward standardization, and increases consistency. Designed to guide the clinic’s contouring practice toward consensus and guideline compliance.
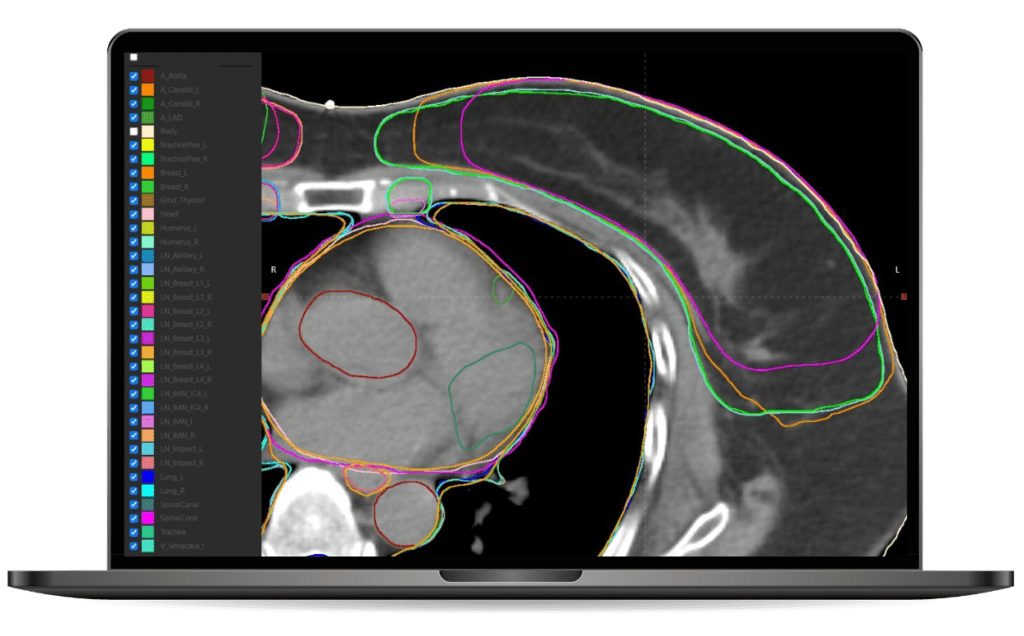
Comprehensive AI contouring solution
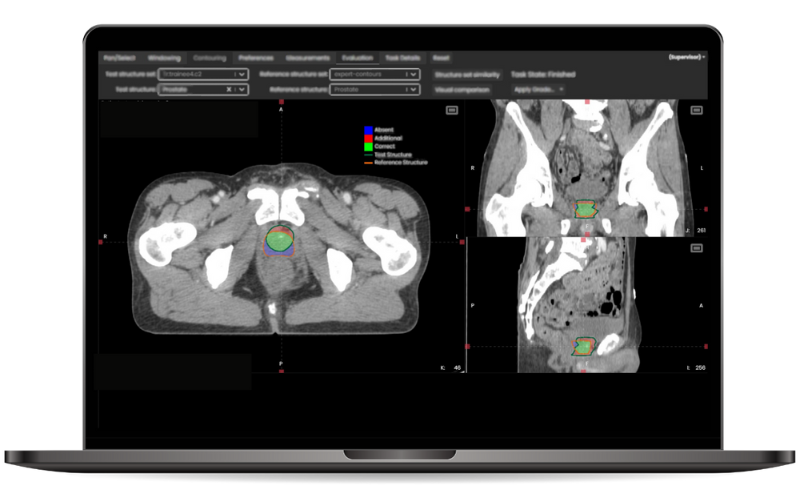
Contour+ encompasses all major anatomical sites and treatment planning structures with state-of-the-art 3D AI models. The models cover over 250 standard and complex structures, such as lymph nodes, bowel loops, and brachial plexus, as well as anatomical landmarks. These structures are tightly aligned with international contouring guidelines provided by RTOG, ESTRO, UK SABR Consortium, and many others.
Auto-Contouring Features

Standardized
Models trained with only peer-reviewed contouring data according to consensus guidelines: ESTRO, EPTN, RTOG, UK SABR Consortium.

Multi-environment deployment
Cloud-based and local, fully integratable with all hospital systems.
Time-saving
A reduction of up to 95% in contouring time per patient.

Reliable
Accurate, fast and reliable contours of 250+ ROIs, including 60+ lymph node areas.

Certified
CE-marked, FDA-Cleared*, QMS is MDSAP and ISO 13485 certified.
Contour+ availability may vary by country. Consult with our experts or distributors to confirm whether Contour+ is accessible in your region.
*MR models and version 1.2.4 models are subject to 510(k) clearance for US customers.
FAQ
How is the segmentation model selected?
The model can be selected by either using individual AE titles that call a specific model or the model can be selected by using one AE title that uses the DICOM tags of the scan to select the model based on predefined model mapping. The former method is most commonly used on the CT scanner. Individual AE titles are customizable. In our web interface there is the option for manual model selection or automatic selection based on the DICOM tags.
How is the data anonymized and how does the MVision connect the structure set to the right patient?
The connection server called MVision Daemon will de-identify the patient’s personal data from the images and create an alternative identification before it sends them to the MVision cloud service as pseudonymized and encrypted. When the Daemon receives the finalized structure set, it connects them to the right patient using the alternative identification. Our web interface has the same functionality, but the pseudonymization is done in the browser and stored in temporary memory (deleted upon closing of the browser).
How long does it take to create the segmentation?
Only a few minutes. The amount of slices and the complexity of the model affects the time a little.
How can the product be customized to meet the clinic’s preferences?
The colors and names of the structures can be customized, and it is possible to exclude unwanted structures from the models. You can also define multiple sub-configurations for each model.
How does the product handle imaging artifacts?
For example dental fillings, pacemaker wires and hip implants are included in the training data, so the AI can create accurate structures despite the artifact. Bilateral hip implants can cause errors, especially if no artifact removal has been used in CT image reconstruction.
Does MVision need additional data from the customer before the product can be used?
The product is ready to use without additional data.
Is there a slice thickness you recommend to images?
There is not one specific thickness we recommend. It does work on 0.5 mm and thicker. If the slice thickness goes up to 5mm and beyond, then some small structures can be missed.
Can the AI handle a scan with variable slice thicknesses?
The slice thickness has to be the same throughout the whole scan. E.g. if a head and neck scan has 1 mm on the neck area, and 3 mm in the shoulder area, it cannot create the structures.
How does MVision compare to other products?
Better quality, largest selection of ROIs, company is dedicated to auto-segmentation. With consistent training data, we verify all training data is done the same way and follows the guidelines, eliminating errors in the training data.
What architecture do your segmentation models use?
The DL algorithm uses an encoder-decoder model architecture. The encoder is based on SE-ResNeXt-50 with a 32x4d template model, and the decoder consists of DenseNet modules. The model processes the scans in thin overlapping sections. Multiple encoders are used to expand the receptive field in the axial direction and the feature maps from each stage of global encoders are gradually merged with the features from the local encoders.
Guide
Explore More
Testimonials
Hear what people say about us.





Customer Portfolio