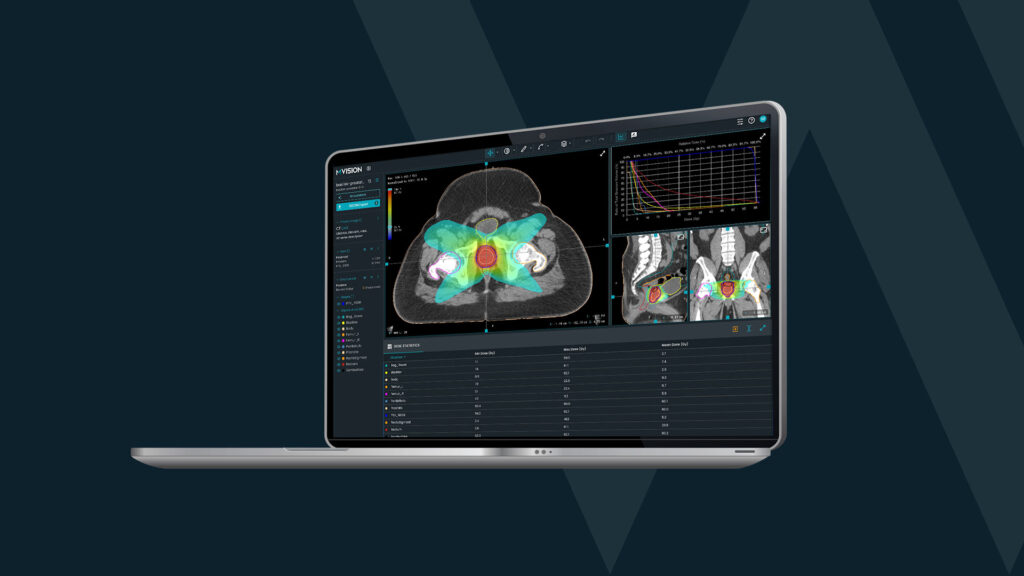
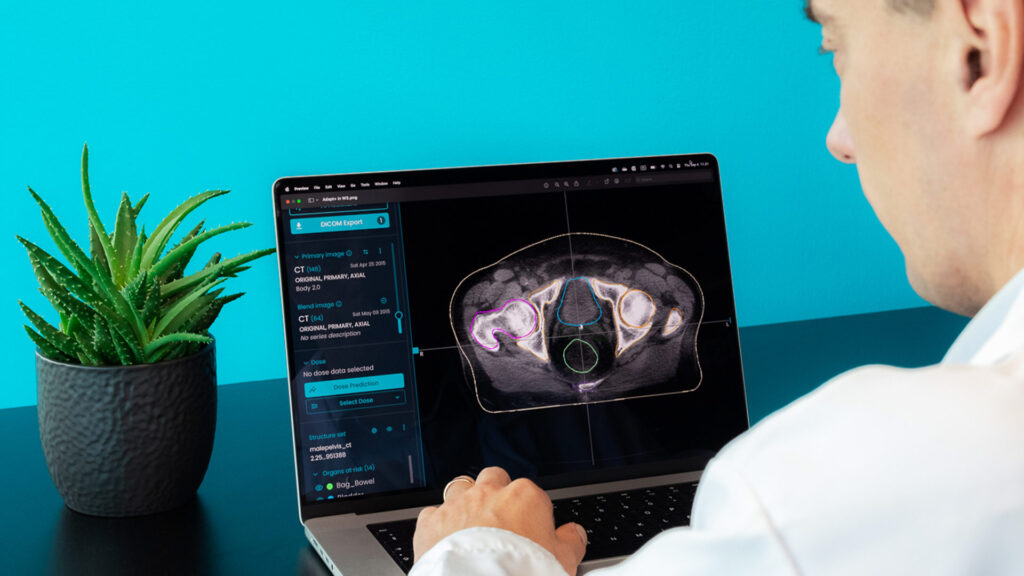
The rising burden of cancer and the radiation therapy workforce crisis create a pressing need for enhanced capabilities and better time management. Technology, in general, and especially AI capabilities, offers new and efficient solutions.
Multiple studies have reported improved time-related metrics after implementing integrated or automated platforms. Key steps in the radiation therapy workflow, including contouring, planning, and quality control, can benefit from automation, with published results demonstrating the impact.
Contouring
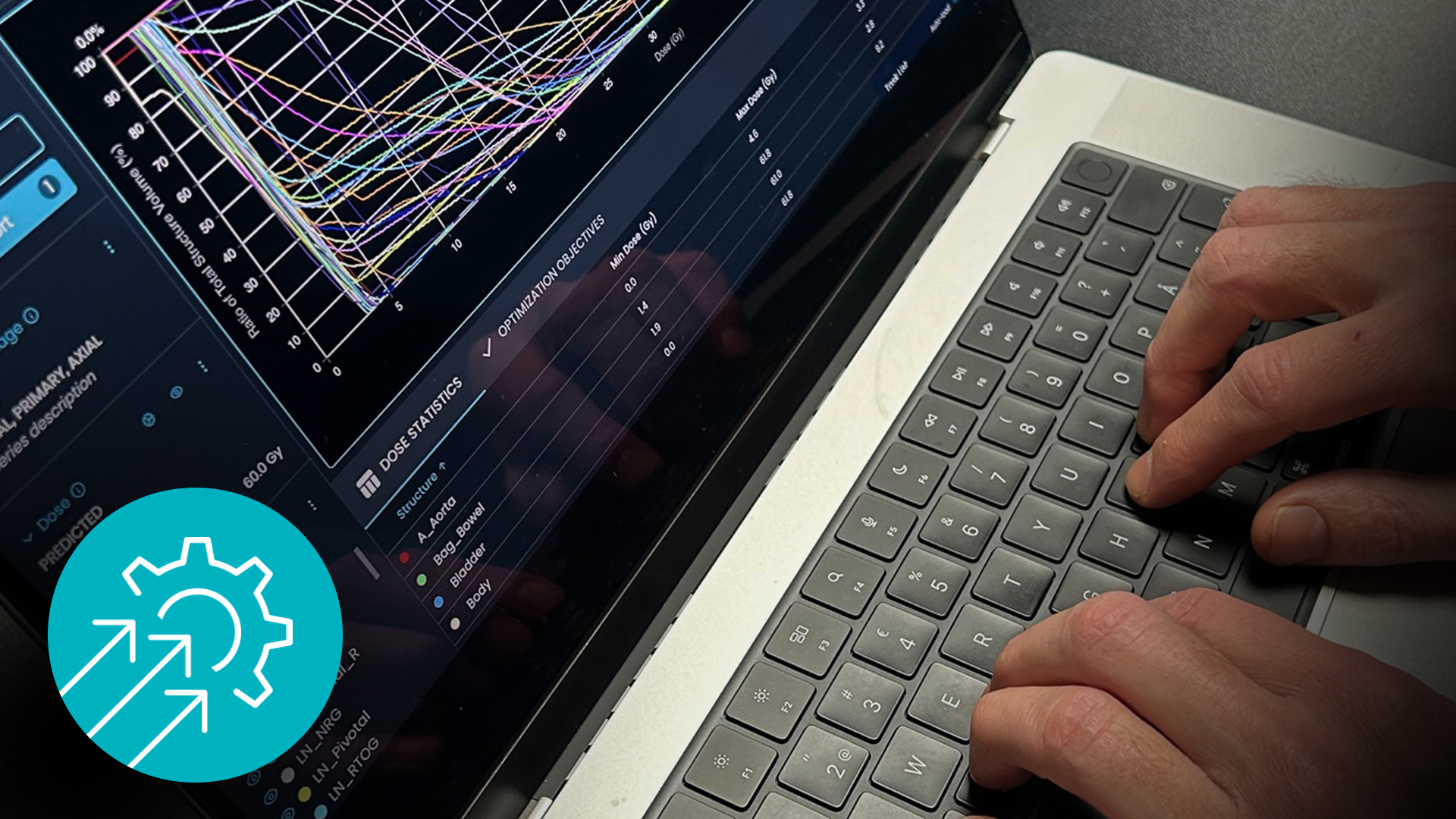
Several studies have shown substantial reductions in contouring time with automated segmentation tools. In evaluations that included Contour+, the extent of time savings varied by tumor site, case complexity, and local protocols. When reported as absolute values, savings reached up to 172 minutes, and percentage reductions reached up to 99% (1,2).
For adaptive treatments, generating new structures or adapting existing ones with AI-based solutions can further improve workflow efficiency. Several AI-driven approaches are now used to support adaptive workflows. Adapt+ is a new module integrated into MVision AI Workspace+ that enables rapid contour adaptation to anatomical changes.
Planning time
Automation has been shown to reduce planning time for over 10 years. A study published in 2014 showed a 5-6 minute reduction for automated IMRT breast cancer plans. The authors also noted an increase in clinical acceptability of plans when shifting from semi-automated inverse planning to fully automated methods (3).
More recently, a comprehensive dosimetric and clinical evaluation compared automatically generated plans with historically accepted, manually generated plans. The researchers included complex cases such as head and neck, high-risk prostate and endometrial cancers, and reported a time reduction of 60-80% compared with manual planning. Additionally, 94% of automated plans scored at least as well as manual plans. Moreover, dose conformity improved, and the integral dose decreased by 6-10% while maintaining similar target coverage (4).
AI can further improve planning automation by predicting doses tailored to patient anatomy. MVision AI’s Dose+, for example, provides AI dose prediction for high-quality prostate cancer treatment planning.
Treatment plan quality control
Implementing automated quality control for treatment planning reduced the process time from 16:20 minutes ±8:50 to 12:00 minutes ±9:20 in a retrospective evaluation of 322 consecutive plans (5).
The overall effect of faster processes is reduced patient waiting time. A complex analysis of the impact of a customized care pathway by implementing templates and checklists concluded that there was a statistically significant improvement in on-time completion rates from 81.9% to 89.7% by decreasing contouring time (from 1.94 to 1.64 days) and treatment planning time (from 0.81 to 0.55 days) (6).
Although the studies mentioned above were conducted in different settings and used various tools, they share a common finding. Their results show that standardization, automation, and implementation of new solutions are helping radiation therapy teams to save time. These outcomes are relevant for both healthcare providers and patients, and demonstrate the value of standardized, automated workflows.
References
- Strolin S, Santoro M, Paolani G, et al. How smart is artificial intelligence in organs delineation? Testing a CE and FDA-approved Deep-Learning tool using multiple expert contours delineated on planning CT images. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1089807. Published 2023 Mar 2. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1089807
- Malone, C., Nicholson, J., Ryan, S., Thirion, P., Woods, R., McBride, P., McArdle, O., Duane, F., Hanna, G. G., McClean, B., & Brennan, S. (2025). Real world ai-driven segmentation: Efficiency gains and workflow challenges in radiotherapy. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 209, 110977.
- Purdie TG, Dinniwell RE, Fyles A, Sharpe MB. Automation and intensity modulated radiation therapy for individualized high-quality tangent breast treatment plans. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;90(3):688-695. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.06.056
- Cilla S, Ianiro A, Romano C, et al. Template-based automation of treatment planning in advanced radiotherapy: a comprehensive dosimetric and clinical evaluation. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):423. Published 2020 Jan 16. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-56966-y
- Jensen, N.K., Boye, K., Damkjaer, S., & Wahlstedt, I. (2018). Impact of Automation in External Beam Radiation Therapy Treatment Plan Quality Control on Error Rates and Productivity. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics.
- Wang Z, Yun Q, Liu C, et al. Improving radiotherapy safety and efficiency with the customized ARIA oncology information system. J Xray Sci Technol. 2021;29(6):1103-1112. doi:10.3233/XST-210952